research use only
TCF12/HEB Antibody [G2F21]
Cat.No.: F6098
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP, IHC |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 85 kDa |
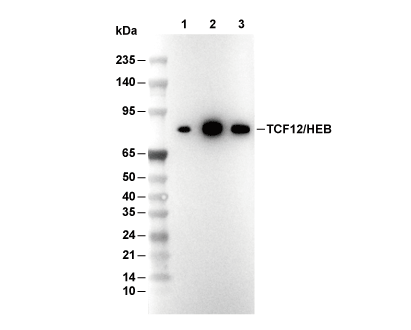
| Positive Control | Human esophageal carcinoma; Human colon adenocarcinoma; Human squamous cell carcinoma of the skin; Human prostate adenocarcinoma; Human lymph node; Human placenta; Human esophagus; IMR-32 cells; Jurkat cells; MLT-4 cells |
|---|---|
| Negative Control | MDA-MB-468 cells |
Experimental Methods
| WB |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample preparation
1. Tissue: Lyse the tissue sample by adding an appropriate volume of ice-cold RIPA/Nuclear Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail),and homogenize the tissue at a low temperature. 2. Adherent cell: Aspirate the culture medium and wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/Nuclear Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 3. Suspension cell: Transfer the culture medium to a pre-cooled centrifuge tube. Centrifuge and aspirate the supernatant. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/Nuclear Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 4. Place the lysate into a pre-cooled microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 4°C for 15 min. Collect the supernatant;
5. Remove a small volume of lysate to determine the protein concentration;
6. Combine the lysate with protein loading buffer. Boil 20 µL sample under 95-100°C for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min after cool down on ice.
Electrophoretic separation
1. According to the concentration of extracted protein, load appropriate amount of protein sample and marker onto SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis. Recommended separating gel (lower gel) concentration: 10%. Reference Table for Selecting SDS-PAGE Separation Gel Concentrations 2. Power up 80V for 30 minutes. Then the power supply is adjusted (110 V~150 V), the Marker is observed, and the electrophoresis can be stopped when the indicator band of the predyed protein Marker where the protein is located is properly separated. (Note that the current should not be too large when electrophoresis, too large current (more than 150 mA) will cause the temperature to rise, affecting the result of running glue. If high currents cannot be avoided, an ice bath can be used to cool the bath.)
Transfer membrane
1. Take out the converter, soak the clip and consumables in the pre-cooled converter;
2. Activate PVDF membrane with methanol for 1 min and rinse with transfer buffer;
3. Install it in the order of "black edge of clip - sponge - filter paper - filter paper - glue -PVDF membrane - filter paper - filter paper - sponge - white edge of clip"; 4. The protein was electrotransferred to PVDF membrane. ( 0.45 µm PVDF membrane is recommended ) Reference Table for Selecting PVDF Membrane Pore Size Specifications Recommended conditions for wet transfer: 200 mA, 120 min. ( Note that the transfer conditions can be adjusted according to the protein size. For high-molecular-weight proteins, a higher current and longer transfer time are recommended. However, ensure that the transfer tank remains at a low temperature to prevent gel melting.)
Block
1. After electrotransfer, wash the film with TBST at room temperature for 5 minutes;
2. Incubate the film in the blocking solution for 1 hour at room temperature;
3. Wash the film with TBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Antibody incubation
1. Use 5% skim milk powder to prepare the primary antibody working liquid (recommended dilution ratio for primary antibody 1:1000), gently shake and incubate with the film at 4°C overnight; 2. Wash the film with TBST 3 times, 5 minutes each time;
3. Add the secondary antibody to the blocking solution and incubate with the film gently at room temperature for 1 hour;
4. After incubation, wash the film with TBST 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Antibody staining
1. Add the prepared ECL luminescent substrate (or select other color developing substrate according to the second antibody) and mix evenly;
2. Incubate with the film for 1 minute, remove excess substrate (keep the film moist), wrap with plastic film, and expose in the imaging system. |
| IHC |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Deparaffinization/Rehydration
1. Deparaffinize/hydrate sections:
2. Incubate sections in three washes of xylene for 5 min each.
3. Incubate sections in two washes of 100% ethanol for 10 min each.
4. Incubate sections in two washes of 95% ethanol for 10 min each.
5. Wash sections two times in dH2O for 5 min each.
6.Antigen retrieval: For Citrate: Heat slides in a microwave submersed in 1X citrate unmasking solution until boiling is initiated; continue with 10 min at a sub-boiling temperature (95°-98°C). Cool slides on bench top for 30 min.
Staining
1. Wash sections in dH2O three times for 5 min each.
2. Incubate sections in 3% hydrogen peroxide for 10 min.
3. Wash sections in dH2O two times for 5 min each.
4. Wash sections in wash buffer for 5 min.
5. Block each section with 100–400 µl of blocking solution for 1 hr at room temperature.
6. Remove blocking solution and add 100–400 µl primary antibody diluent in to each section. Incubate overnight at 4°C.
7. Remove antibody solution and wash sections with wash buffer three times for 5 min each.
8. Cover section with 1–3 drops HRPas needed. Incubate in a humidified chamber for 30 min at room temperature.
9. Wash sections three times with wash buffer for 5 min each.
10. Add DAB Chromogen Concentrate to DAB Diluent and mix well before use.
11. Apply 100–400 µl DAB to each section and monitor closely. 1–10 min generally provides an acceptable staining intensity.
12. Immerse slides in dH2O.
13. If desired, counterstain sections with hematoxylin.
14. Wash sections in dH2O two times for 5 min each.
15. Dehydrate sections: Incubate sections in 95% ethanol two times for 10 sec each; Repeat in 100% ethanol, incubating sections two times for 10 sec each; Repeat in xylene, incubating sections two times for 10 sec each.
16. Mount sections with coverslips and mounting medium.
|
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| TCF12/HEB Antibody [G2F21] detects endogenous levels of total TCF12/HEB protein. |
| Subcellular Location |
|---|
| Nucleus |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| Q99081 |
| Clone |
|---|
| G2F21 |
| Synonym |
|---|
| TCF12; Transcription factor 12; TCF-12; Class B basic helix-loop-helix protein 20 (bHLHb20); DNA-binding protein HTF4; E-box-binding protein; Transcription factor HTF-4; BHLHB20; HEB; HTF4 |
| Background |
|---|
| TCF12/HEB (Transcription Factor 12/HeLa E-box Binding protein) is a class I E-protein basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor encoded by TCF12 at chromosome 15q21, existing in two major isoforms: HEBCan (681 amino acids, from the ubiquitous promoter) and HEBAlt (short form, from a distal promoter). These isoforms heterodimerize with tissue-specific bHLH partners such as E47, MyoD, and NeuroD via their conserved bHLH domain, which consists of a basic DNA-binding region and an HLH motif for dimerization, to recognize CANNTG E-box consensus sequences, thereby driving lineage commitment in T/B cells, muscle, and neurons. TCF12/HEB contains an N-terminal activation domain rich in acidic residues for coactivator recruitment, a central transactivation domain with glutamine/proline stretches that enhance RNA polymerase II pausing and release, the core bHLH domain (~60 residues) where the basic helix contacts the major groove of DNA while HLH amphipathic helices dimerize through hydrophobic interfaces, and C-terminal inhibitory domains that modulate partner specificity. Alternative splicing at exon 1 generates HEBCan for broad T cell developmental stages and HEBAlt, which is enriched in DN2/DN3 thymocytes to promote efficient precursor generation. TCF12/HEB orchestrates T cell development by co-binding Lmo2 and Lyl1 at Eβ and Cd4 enhancers to activate genes involved in recombination and expansion, represses E2A targets through competitive dimerization to limit self-renewal, and balances hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) reconstitution versus differentiation, with deficiency resulting in myeloid bias, B/T cell blockage, and proliferation defects. PKCθ/Carma1 signaling phosphorylates HEBCan at serine residues, relieving Id protein-mediated autoinhibition and enabling TCR-induced chromatin looping with Runx1 and Foxp1 for Il2ra and Dtx1 expression, while HEBAlt uniquely partners with Bcl11b at the Tcrα enhancer to facilitate positive selection. TCF12 mutations cause coronal craniosynostosis (Saethre-Chotzen syndrome) by disrupting Twist1 heterodimerization and suture patency; haploinsufficiency is linked to dyslexia through neurodevelopmental gene dysregulation, and somatic alterations contribute to leukemia (AML1-ETO fusions) or solid tumor progression via EMT and invasion. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.