research use only
Menadione (Vitamin K3) phosphatase inhibitor
Cat.No.S1949
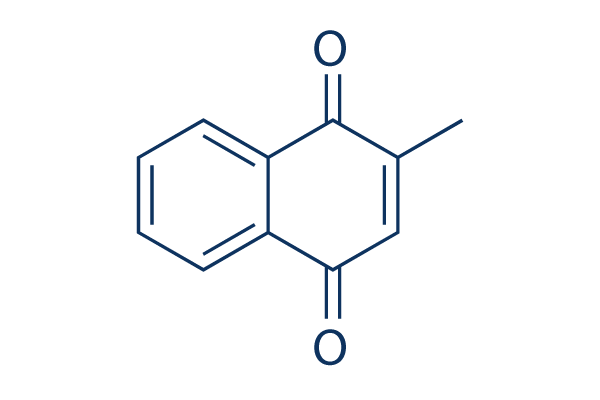
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 172.18
Quality Control
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HT22 cells | Function assay | Neuroprotective activity in mouse HT22 cells assessed as prevention from glutamate-induced oxidative cell death by MTS assay, PD50=0.797 μM | ||||
| HeLa cell | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against HeLa cell lines, EC50=3.7 μM | ||||
| PaCa2 cell | Proliferation assay | Antiproliferative activity against human pancreatic carcinoma Mia PaCa2 cell line by colorimetric assay, IC50=6.2 μM | ||||
| HT-29 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human HT-29 cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=9.69 μM | |||
| DU145 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human DU145 cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=9.86 μM | |||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human MDA-MB-231 cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=12.68 μM | |||
| human A2058 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human A2058 cells assessed as inhibition of formazan formation at day 5 by measuring absorbance at 430 nm, IC50=13.4 μM | ||||
| SAS cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 h | Cytotoxicity against human SAS cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=14 μM | |||
| HaCaT cells | Function assay | 48 h | Antihyperproliferative activity against human HaCaT cells assessed as inhibition of cell growth after 48 hrs by phase contrast microscopy, IC50=15.8 μM | |||
| HeLa cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 h | Cytotoxicity against human HeLa cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=18 μM | |||
| CRL2796 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human CRL2796 cells assessed as inhibition of formazan formation at day 4 by measuring absorbance at 430 nm, IC50=21 μM | ||||
| HL60 cells | Function assay | 50 μM | Induction of necrosis in intact human HL60 cells assessed as cytosolic LDH release at 50 uM | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 172.18 | Formula | C11H8O2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 58-27-5 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | NSC 4170 | Smiles | CC1=CC(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2C1=O | ||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 34 mg/mL
(197.46 mM)
Ethanol : 34 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Cdc25 phosphatase
DNA polymerase γ
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Menadione (Vitamin K3) prevents mitochondrial Ca(2+) uptake in normal pancreatic acinar cells, which permits rapid spread of Ca(2+) throughout the cell. Its-induced mitochondrial depolarisation is due to induction of the permeability transition pore. At nontoxic concentration, this compound results in a brief activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in the RALA255-10G rat hepatocyte cell line. It is equipotent against multidrug-resistant and parental leukemia cell lines with IC50 values of 13.5 mM and 18 mM, respectively. The compound inhibits the incorporation of radioactive thymidine, uridine and amino acids into DNA, RNA and protein, respectively, in three humancancer cell lines. At 1-20 mM, it dose- and time-dependently inhibits cell proliferation of AR4-2J cells. A concentration of 100 mM causes rapid cell death. This level (100 mM) induces DNA smear in electrophoresis indicative of necrosis, while lower concentrations (10-20 mM) induces a DNA ladder indicative of apoptosis. Concentrations of 1-20 mM induce wild-type P53, whereas 100 mM has a minor effect on wild-type P53. Treatment with it clearly affects the mitochondrial function of Jurkat T cells by inducing a collapse of the inner transmembrane potential (DeltaPsi(m)) and a decrease in inner membrane mass, which could be completely reversed by N-acetylcysteine. |
References |
|
Applications
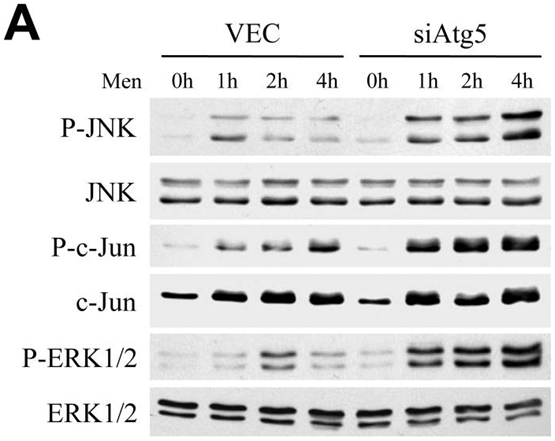
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-JNK / JNK / p-c-Jun / c-Jun / p-ERK / ERK Cyclin B1 / CDK1 / CDC25C c-Fos / HO-1 |
|
20578144 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01094444 | Completed | Folliculitis |
Per Pfeiffer|Odense University Hospital |
May 2010 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00656786 | Completed | EGFR Inhibitor-associated Rash |
Spectrum Pharmaceuticals Inc |
April 3 2008 | Phase 1 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
