research use only
Sumatriptan Succinate 5-HT Receptor agonist
Cat.No.S1432
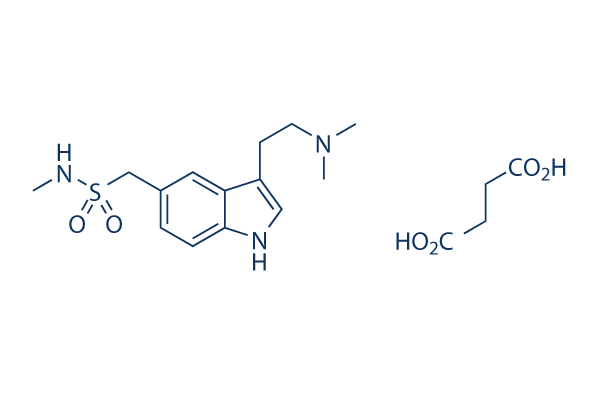
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 413.49
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Adrenergic Receptor AChR COX Calcium Channel Histamine Receptor Dopamine Receptor GABA Receptor TRP Channel Cholinesterase (ChE) GluR |
|---|---|
| Other 5-HT Receptor Inhibitors | WAY-100635 Maleate Serotonin (5-HT) HCl Puerarin BRL-15572 Dihydrochloride SB269970 HCl Ketanserin RS-127445 Nuciferine Flopropione BRL-54443 |
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 413.49 | Formula | C14H21N3O2S·C4H6O4 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 103628-48-4 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | GR 43175 | Smiles | CNS(=O)(=O)CC1=CC2=C(C=C1)NC=C2CCN(C)C.C(CC(=O)O)C(=O)O | ||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 83 mg/mL
(200.73 mM)
Water : 83 mg/mL Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
5-HT
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Sumatriptan displays the highest affinity for 5-HT1D (Ki = 17 nM) and 5-HT1B (Ki = 27 nM) binding sites and is slightly less potent at 5-HT1A binding sites (Ki = 100 nM). Sumatriptan markedly attenuates plasma protein extravasation induced by electrical trigeminal ganglion stimulation. Sumatriptan reduces morphological changes in post-capillary venules and mast cells within dura mater following electrical trigeminal ganglion stimulation.
|
| In vivo |
Sumatriptan at a clinically relevant dose (100 mg/kg, s.c.) leads to a significant reduction of the mechanical allodynia-like behaviour on both the injured and the contralateral sides (peak-effects 6.3 g and 4.4 g, respectively) in a rat model of trigeminal neuropathic pain. Sumatriptan reduces the numbers of Fos-positive cells found in laminae I and IIo of the trigeminal nucleus caudalis and C2 (6, 13 cells and 9 cells, respectively) after mechanical stimulation in cats. Sumatriptan constricts selectively the cranial vessels that are distended and inflamed during migraine, the action is mediated by activation of a 5-HT1 receptor subtype which has been shown in animals to be localized in cranial vessels. Sumatriptan results in oral bioavailabilities of 37, 58 and 23% in rat, dog and rabbit, respectively. Sumatriptan is cleared rapidly by metabolic and renal clearance with a half-life of 1-2 hour in rat, dog and rabbit. Sumatriptan produces few adverse pharmacodynamic effects when administered acutely, except at high doses, although it is less well tolerated in dogs.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
