research use only
Hydroxyzine 2HCl Histamine Receptor antagonist
Cat.No.S4026
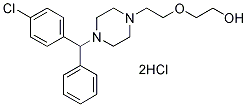
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 447.83
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Adrenergic Receptor AChR 5-HT Receptor COX Calcium Channel Dopamine Receptor GABA Receptor TRP Channel Cholinesterase (ChE) GluR |
|---|---|
| Other Histamine Receptor Inhibitors | GSK2879552 Dihydrochloride JNJ-7777120 Ebastine Ciproxifan Maleate Mianserin HCl Astemizole Lafutidine Mizolastine Rupatadine Fumarate Betahistine 2HCl |
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 447.83 | Formula | C21H27ClN2O2.2HCl |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 2192-20-3 | -- | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | C1CN(CCN1CCOCCO)C(C2=CC=CC=C2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl.Cl.Cl | ||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 90 mg/mL
(200.96 mM)
Water : 90 mg/mL Ethanol : 15 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Histamine H1 receptor
10 nM-19 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Hydroxyzine inhibits carbachol (10 μM)-induced serotonin release by 34% at 10 μM, by 25% at 1 μM and by 17% at 0.1 μM in pretreated bladder slices for 60 min. Hydroxyzine (0.1 mM) treatment inhibits the progression and severity of EAE by 50% and the extent of mast cell degranulation by 70% in Lewis rats with allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE). Hydroxyzine (500 µM) significantly increases transport of etoposide to the serosal site in the jejunal everted sacs. Hydroxyzine significantly reduces the efflux and approximately 2.4 µg/mL of etoposide in the jejunum and ileum. Hydroxyzine (0.2 μg/mL) significantly enhances the efflux of RH123 to the lumen.
|
| In vivo |
Hydroxyzine (500 μM) significantly decreases the steady-state etoposide concentration 2-fold, where the steady-state concentration reached about 0.055 μM/mL in Sprague-Dawley rats. Hydroxyzine (12.5 mg/kg, 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg i.p.) shows little direct analgesic activity but markedly potentiates only the effect of morphine on the vocalization after-discharge which represents the affective component of pain in rats. Hydroxyzine (50 mg/kg i.p.) potentiates morphine on the tail-flick test, while Hydroxyzine (12.5 mg/kg i.p.) decreases morphine antinociception in rats.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04188106 | Completed | Smoking Cessation|Stress|Sleep Disturbance|Nausea |
Rose Research Center LLC|Foundation for a Smoke Free World INC |
June 17 2019 | Phase 4 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
