research use only
Simvastatin (MK-733) HMG-CoA Reductase inhibitor
Cat.No.S1792
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 418.57
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Dehydrogenase HSP Transferase P450 (e.g. CYP17) PDE phosphatase PPAR Vitamin Carbohydrate Metabolism Mitochondrial Metabolism |
|---|---|
| Other HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors | Mevastatin SR-12813 Clinofibrate Dihydrolanosterol 7-ketocholesterol Cerivastatin sodium |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rat liver hepatocytes | Function assay | 4 h | Inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in rat liver hepatocytes after 4 hrs, IC50=1.3 nM | |||
| rat L6 cells | Function assay | Inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in rat L6 cells assessed as incorporation of [14C]acetate into cholesterol, IC50=0.027 μM | ||||
| HepG2 cells | Function assay | In vitro inhibitory activity was evaluated on cholesterol biosynthesis in HepG2 cells, IC50=0.04 μM | ||||
| HEK293 cells | Function assay | Inhibition of OATP1B1 (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells using estradiol-17beta-glucuronide substrate, IC50=4.4 μM | ||||
| human A549 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=16.3 μM | |||
| human HS68 cells | Cytotoxic assay | Cytotoxicity against human HS68 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=26.4 μM | ||||
| mouse MEF cells | Cytotoxic assay | Cytotoxicity against mouse MEF cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=36.7 μM | ||||
| RASMC cells | Function assay | 2 μM | 72 h | Inhibition of rat Ftase in RASMC cells assessed as reduction in Ras prenylation at 2 uM after 72 hrs by Western blot analysis | ||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 418.57 | Formula | C25H38O5 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 79902-63-9 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | MK 733 | Smiles | CCC(C)(C)C(=O)OC1CC(C=C2C1C(C(C=C2)C)CCC3CC(CC(=O)O3)O)C | ||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 83 mg/mL
(198.29 mM)
Ethanol : 83 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
HMG-CoA reductase
(Cell-free assay) 0.1-0.2 nM(Ki)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Prior to use in cell assays, Simvastatin needs to be activated by NaOH in EtOH treatment. This compound inhibits cholesterol synthesis in mouse L-M cell (fibroblast), rat H4II E cell (liver), and human Hep G2 cell (liver) with IC50 of 19.3 nM, 13.3 nM and 15.6 nM, respectively. This compound treatment leads to a dose-dependent increase in serine 473 phosphorylation of Akt within 30 minutes, with maximal phosphorylation occurring at 1.0 µM. It (1.0 µM) enhances phosphorylation of the endogenous Akt substrate endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), inhibits serum-free media undergo apoptosis and accelerates vascular structure formation. This chemical displays anti-inflammatory effects in vitro. It (10 µM) reduces anti-CD3/anti-CD28 antibody-stimulated proliferation of PB-derived mononuclear cells and synovial fluid cells from rheumatoid arthritis blood, as well as IFN-γ release. This compound (10 µM) suppresses cell-mediated macrophage TNF-γ release induced via cognate interactions by ~30%. |
| Kinase Assay |
HMG-CoA reductase activity assay
|
|
The total volume of each assay is 95 μL and the reaction mixture contained 10 μL of the inhibiting compound to be tested and 85 μL of the incubating buffer containing 2 mg/mL liver microsomes, 0.1 M KH2PO4, pH 7.2, 5.7 mM dithiothreitol, 10 mM glucose-6-phosphate, 2 U/mL glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, 1 mM NADP, 10 μM miconazole. Control experiments are done without NADPH generating system. All samples are incubated 10 min at 37 ℃ before addition of 5 μL of substrate (unlabelled and 14C-HMG-3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl CoA, final concentration 50 μM, 2.5 nCi/nmole). After 30 min at 37 ℃, the reaction is stopped by adding 27 μL 1N HCl and 20 μL of unlabelled mevalonolactone (200 μg/assay). The conversion of mevalonic acid to lactone is performed at room temperature for 60 min.
|
|
| In vivo |
Simvastatin orally administration inhibits the conversion of radiolabeled acetate to cholesterol with IC50 of 0.2 mg/kg. This compound (4 mg/day) orally administration for 13 weeks to rabbits fed an atherogenic cholesterol-rich diet, returns the cholesterol-induced increases in total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol to normal level. This compound (6 mg/kg) produces an increase in LDL receptor-dependent binding and increases the number of hepatic LDL receptors in rabbits fed a diet containing 0.25% cholesterol. This compound influences inflammation independent of its effect on plasma cholesterol level. In cynomolgus monkeys consumed an atherogenic diet, this compound (20 mg/kg/day) induces a 1.3-fold less macrophage content in lesions, and 2-fold less vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, interleukin-1beta, and tissue factor expression, accompanied by a 2.1-fold increases in lesional smooth muscle cell and collagen content. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | Nrf2 p-RB / Cyclin D1 / p21 / p27 / PCNA / CDC45 AMPK / p-AMPK / P70S6 / p-P70S6 / LC3 / Atg7 Bcl-2 / PARP / Caspase-3 / Cleaved Caspase-3 HMGCR |
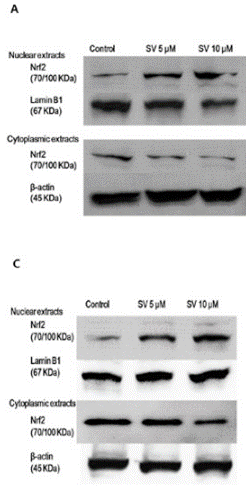
|
27323826 |
| Immunofluorescence | Nrf2 LC3A/B |
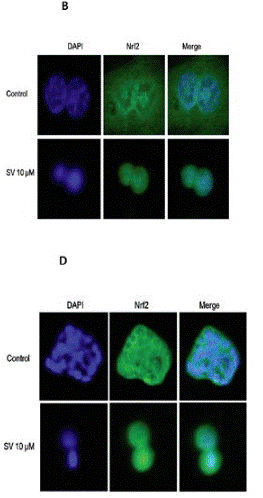
|
27323826 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
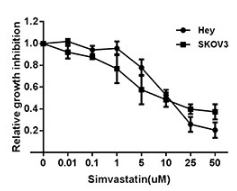
|
26503475 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05771675 | Not yet recruiting | Recurrent Acute Pancreatitis|Chronic Pancreatitis |
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center|United States Department of Defense |
January 2024 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT05542095 | Withdrawn | Olfactory Disorder|COVID-19 |
Washington University School of Medicine|Duke University |
May 1 2023 | Phase 1 |
| NCT06207682 | Completed | Healthy Volunteers |
Amgen |
June 28 2022 | Phase 1 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
Can you please advise if it has been tested effectively for in vivo use in mice? What solvent can be used to deliver this compound in vivo?
Answer:
This compound is an oral drug and a lot of studies report its use in mice. According to this paper (http://atvb.ahajournals.org/content/21/1/115.full), 0.5% Methyl-cellulose can be used as the vehicle.
Question 2:
If any specific protocols exist for in vitro use, specifically any steps required to activate it?
Answer:
This compound is supplied in an inactive form and requires treatment with NaOH in EtOH followed by neutralization to pH 7.2 for activation. Please find the details from the following reference: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2739764/.
