research use only
Safinamide Mesylate MAO inhibitor
Cat.No.S1472
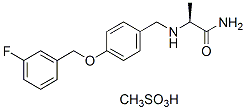
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 398.45
Quality Control
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 398.45 | Formula | C17H19FN2O2.CH4O3S |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 202825-46-5 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | PNU-151774E,FCE28073 | Smiles | CC(C(=O)N)NCC1=CC=C(C=C1)OCC2=CC(=CC=C2)F.CS(=O)(=O)O | ||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 80 mg/mL
(200.77 mM)
Water : 80 mg/mL Ethanol : 13 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
Greater than 5,000-fold potency in inhibiting MAO-B vs. MAO-A.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
MAO-B
98 nM
|
| In vitro |
Safinamide is a highly selective MAO-B inhibitor in rat brain mitochondria, with an IC50 of 98 nM. Safinamide inhibits MAO-B in human brain with an IC50 of 9 nM. Safinamide has high affinity for the Na+ channel-binding site II in rat cortical membranes, with an IC50 of 8 μM. Safinamide inhibits the fast Na+ currents in a concentration- and state-dependent manner in rat cortical neurons. Safinamide blocks N-Type Ca2+ currents in rat cortical neurons with IC50 of 23 μM. Safinamide inhibits glutamate release induced by depolarizing conditions in rat hippocampal synaptosomes with IC50 of 9 μM. Safinamide incubated 1 hour before veratridine reduces the neuron damage with an IC50 1.4 μM through blockade of opening voltage-dependent Na+ and Ca2+ channels in rat primary cortical neurons. Safinamide binds to human MAO B with a Ki of 0.5 μM. Safinamide binds to human MAO B in an extended conformation occupying both flavin and entrance cavity.
|
| In vivo |
Safinamide orally administrated dose-dependently inhibits mouse brain MAO-B with IC50 of 0.6 mg/kg, and MAO-B activity recovers quickly, starting from 8 hours. Safinamide significantly inhibits cell body degeneration in the substantia nigra pars compacta. Safinamide intraperitoneally administered 15 minutes before kainic acid protects against hippocampal neuron loss, starting at 10 mg/kg showing neuroprotective properties. Safinamide intraperitoneally administrated at dose of 100 mg/kg shows a relevant neurorescuing effect on hippocampal neurons when given 3 hours after ischemia. Safinamide has a high oral bioavailability (80-92%), is rapidly absorbed in plasma after reaching the peak within 0.5-2 hours declines, with a terminal half-life of about 3, 7, and 13 hours in mice, rats, and monkeys, respectively.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
